
How to create a project budget: methods and techniques for effective project budgeting
Learn how to create a project budget with this detailed guide. Discover essential methods and techniques for effective project budgeting in PPM.

To be agile or not to be? That is the question. More and more organizations and departments are adopting Agile methodologies for both project and portfolio management. However, is Agile made for everyone? Is it always justified that CEOs and company executives push Agile methodologies at all costs, without considering the pros and cons of its implementation?
CEOs like the latest technology. CEOs like continuous improvement initiatives. CEOs like to be at the cutting edge of technology whenever possible. They like to make decisions. But are those decisions always in the best interest of the organization? Or are The latest tech, the latest processed, the best buzzwords this week. Whatever is hot now – that’s what they want. They’re pretty sure that’s what will solve whatever problem or change how the organization is going through right now.

AGILE PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
Ensure transparency and strategic alignment for your Agile Portfolios
Learn more about Triskell’s Agile PPM solution
Agile. It’s the latest corporate buzzword making the rounds. One survey last year found that over half the organizations who were implementing it were doing so because the CEO said so, not because of the value it adds. When done well it can transform individuals and organizations, but when done badly it can suck the life out of everyone involved.
So, when the CEO orders a change or champions something like this… what do you do? This topic brings to mind what I would consider an appropriate or applicable quote from the late Steve Jobs… “In weak companies politics win. In strong companies, best ideas do.” Strategic planning is a must – we must avoid falling into the trap of just adapting to the whims of leadership or the latest technology.
If Agile implementation is done badly, it can suck the life of everyone involved
Agile is an iterative type approach where phases (requirements/design/build/test) needed to complete a project are generally done in parallel together. There are many Agile frameworks but each effectively has the same empirical structure where tasks are broken down into small planning cycles. Requirements and solutions are continually evolving and based on priority and discipline.
Generally, the Agile pros outweigh the Agile cons, but let’s consider a few…
WHITE PAPER
Agile Portfolio Management – Making the right decision
Make Agile work in your organization
Request a demo of Triskell and see how it can help you to reap the benefits of Agile while ensuring strategic alignment.
The bottom line is this – Agile can be great for the organization and can be the right software development life cycle (SDLC) to follow. But it must be well adopted among the dev staff and is not necessarily the end all best for everyone and every situation. And it certainly should not be rolled out and forced on a mature development staff just because the CEO heard about it and decided to force it on the organization.
More advanced organizations focus on project outcomes over project outputs
I know that would have been a complete disaster back when I was a younger application developer working with a dev staff that averaged 20 years older than me. The idea would have crashed and burned fast and many projects would have suffered irreparable damage in budget and timeframe.
What are your thoughts? Have you had major changes or processes forced on you by the Ceo’s desire to implement something “just because”? What pushback was done there? Did it work? Please share and discuss.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Get stories like this in your inbox
Request a demo of Triskell Software
Want to learn more? Request a free demo of Triskell Software and you will discover the PPM software that best suits your business needs.
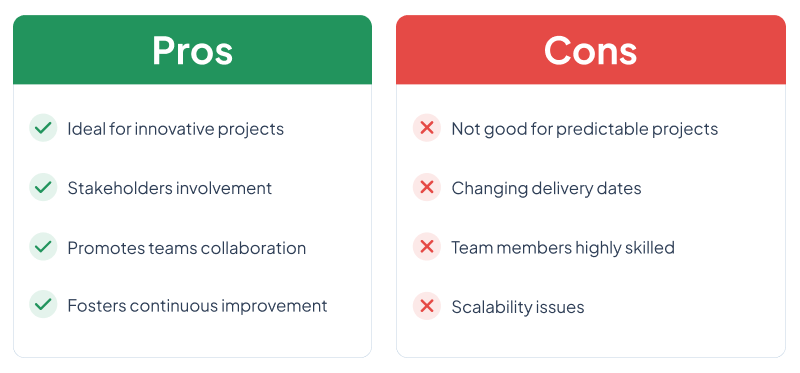
Pros:
Cons:
Agile is a good fit for projects with:
However, if your project has:
Then a traditional project management approach might be more suitable.
If Agile isn’t the best fit for your project, here are some alternative project management approaches:
Here are some tips to mitigate the potential cons of Agile:
Related Content

How to create a project budget: methods and techniques for effective project budgeting
Learn how to create a project budget with this detailed guide. Discover essential methods and techniques for effective project budgeting in PPM.

20 strategic planning models and tools for medium and large companies
Looking for the best strategic planning frameworks? This guide covers 20 proven models to enhance decision-making and business growth.

The ultimate guide to Scenario Analysis for PPM: how it works, examples, techniques and tools
Master scenario analysis for PPM. Discover how to apply scenario planning for resource management, budgeting, and strategic decision-making.
Solutions
Platform
Company
Compare Triskell
© 2025 Triskell Software. All Rights Reserved.
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Cookies policy
Quality Management and Information Security System Policy

We use technologies such as cookies to store and/or access device information. We do this to improve the browsing experience and to display (non-) personalized advertisements. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique ID's on this site. Not consenting, or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.