
Why the CIO needs a PMO approach
Unlock business success: discover why the CIO must embrace a PMO approach! to elevate efficiency and boost productivity.

Why more and more R&D project teams are embracing Phase Gate Process? R&D projects are becoming increasingly important for businesses, regardless of the sector to which they belong. The digital era has created a need for companies to explore market opportunities. They must launch ever more innovative products and services that provide a competitive advantage over their competitors in the shortest possible time and also meet the needs of an increasingly demanding consumer who demands tailor-made products.
While these projects represent a great opportunity for growth for companies, they also entail many risks. Therefore, R&D project management plays a critical role in organizations. Inefficient decision-making on matters such as project feasibility, risk management, capacity planning, resource allocation or the elimination of bottlenecks throughout all phases of the project can lead to project failure.
And this is where the Phase Gate process comes into play, as it will be your best ally in dealing with the challenges you will be facing in R&D project management. In this post, you will learn the basic principles behind the Phase Gate methodology and how R&D project management will benefit from it.
You are probably wondering how the Phase Gate Process can help your organization’s R&D or product development project management. Just by knowing the general guidelines of this methodology, you will realize that it can be applied to any type of project.
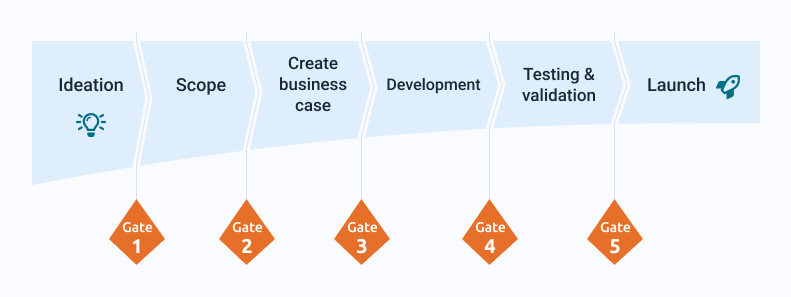
The Phase Gate methodology is applicable to the entire project, from ideation to project closure. It involves reviewing and validating the progress made in each phase of the project before moving on to the next one. In these review processes, project managers should review the progress made and confirm that it is aligned with the requirements established in that specific phase. Based on this analysis, the project team may decide:
Phase Gate consists of reviewing and validating the progress made in each phase of the project
As you can see, it is a methodology that fits like a glove to the challenges that many product or software development teams have to face in their work environment. An environment characterized by the constant evolution of markets and user demands, which forces companies to respond in an agile and flexible manner to new market trends and opportunities that may arise.
Therefore, this phased review process helps organizations to better align their R&D project requirements with these changing market and user needs.
The Phase Gate methodology started its first steps in the United States in the mid-1980s. DuPont and Exxon Chemical were the first major companies to adopt these review processes for each of the phases of their projects.
Both companies belong to the energy sector. But over the years, more and more companies from all types of industries (engineering, software, automotive, healthcare, etc.) adopted the Phase Gate methodology as it became more popular. The phase Gate process can be adapted to projects of a very diverse nature: new product development, software releases, or even Transformation Programs.
Whatever the project type, the Phase Gate methodology consists of 5 distinct phases (which can be 6 even if we include the preliminary ideation phase). They are as follows:
Whether it is an R&D project or any other, it will always start with an ideation phase. Here brainstorming and market research play a key role in helping your team come up with ideas that, once they take shape, can be turned into a project. In order to list the project requirements, it is necessary to already have feedback from customers and users at this early phase.
Once the idea is defined, it is time to evaluate its feasibility, its scope and determine if it can be an interesting market opportunity. The SWOT and PESTEL analyses will be your best ally to give shape to the product idea you have in mind and to visualize its viability in your target market.
When you are clear about the scope, vision and feasibility of the idea, it is time to build a business case with the requirements of the project, including the objectives to be achieved, the phases and the requirements of each of them, and a detailed report on the feasibility of the project.
Here, the business case will be implemented and the development phase of the product prototype will begin. It is important to be clear about the milestones to be achieved during this phase and the KPIs to be monitored during each of the different phases of product development.
Once the prototype is finished, it is in this phase that the pertinent tests and validations are carried out in order to detect possible improvements to the original prototype. This phase also includes usability tests of a beta phase of the product by the customers.
The product has already completed all the previous phases and is being launched on the market. Marketing plays an essential role here, since it has to design a strategy that will allow the product to penetrate its market and catch the attention of potential consumers.
Between each phase is when the review process takes place, in which it is decided whether or not the project moves on to the next phase. The methodology would have, as an outline, the following form:
See the Triskell platform in action in a personal demo
As mentioned earlier, the Phase Gate methodology has been in place for nearly 35 years. Project management has evolved considerably during all this time, especially thanks to the irruption and consolidation of Agile methodologies. These have had a great influence on the Phase Gate process, especially Scrum.
And this influence has resulted in the introduction of new elements in this methodology. This is what is known as the Triple A process, which is composed of:
Thanks to Triple A, you will gain efficiency, quality, and speed in the development of projects
By including these three elements in the R&D projects you are working on, you will gain not only speed in delivery times throughout each of the project phases, but also efficiency and quality with both the development and the outcome of the project.
The main feature of the Phase Gate process is undoubtedly the review process for each phase. In each of them, an assessment is made to determine whether the project should go ahead or not based on a series of criteria that are agreed upon prior to the review process itself, which are as follows:
During each review process, the project team will analyze the progress made so far and will compare it with the specifications detailed in the project documents (Business Case, Project Plan, Product Specification Breakdown, etc.). It will also evaluate the viability or not of the project based on whether there have been changes in the client’s requirements, in the market situation or changes at a political, economic or social level that may affect its profitability.
In each review process, an analysis of the progress made will be analyzed and compared with the project specifications
Once these criteria have been reviewed, a final decision must be made in order to move the project forward to the next phase. Here are four possible options:
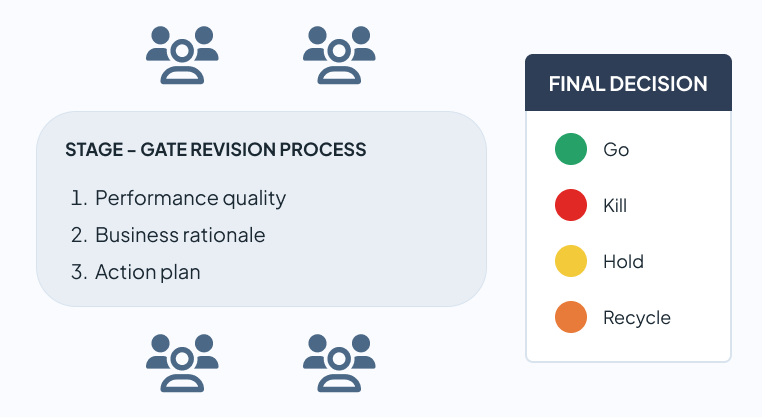
These review processes should be carried out independently from the day-to-day project management. They should involve multidisciplinary profiles so that the project team gets different points of view and can make a decision based on different criteria.
It is recommended that the following people participate:
This review process becomes especially important in R&D projects given the complexity of these projects and how rapidly customer needs and markets can change Thanks to these exhaustive review processes, the Phase Gate methodology provides R&D project teams with the necessary mechanisms to deliver high-quality results and to revise or cancel projects if they no longer follow the agreed roadmap.
Now that you have a general idea of the Phase – Gate process, its different phases, and how the review process of each ‘Phase’ works, you are probably asking yourself the following question: how can this methodology help me to efficiently manage the R&D projects I am currently working on?
There is no room for error in R&D projects. These are the most important projects for the organizations and are considered top priority in their execution. This is why a methodology such as Phase Gate, which allows for retrospective evaluation of the progress made in each phase before moving on to the next, is the best fit for this type of project.
These are the seven benefits of the Phase-Gate Process for R&D Projects:
R&D project execution is really complex. The fact of being able to work with a methodology that makes it possible to review the progress made from time to time and identify areas of improvement and errors to be addressed is a guarantee of success.
And it is not only for the current project and to be able to make modifications on the fly to correct those mistakes. Having processes in place to identify bugs and bottlenecks will also be useful for future R&D projects that you will manage.
This review process to evaluate the progress of each of the project phases is also an excellent opportunity for a more efficient resource management in your R&D projects. For example, Phase Gates can be used for:
Ultimately, with the Phase Gate process, you will maximize the productivity of each of the organization’s resources, assigning them to those project tasks that best fit their skills, and relocating them to other initiatives once they have fulfilled their role in the project.
R&D projects are critical for companies. The reason why many of them fail is due to the fact that unplanned modifications to the initial requirements of the project or the final product may occur at the request or initiative of one of the stakeholders, causing the project to derail.
Many R&D projects fail because unplanned modifications occur in the project requirements
With the review processes of the Phase Gate methodology, you will get all people, teams and stakeholders on the same page about the objectives and requirements of the final product. You will therefore avoid unplanned deviations and mitigate the risks associated with this type of decisions.
One of the major challenges for organizations is to align projects with strategic objectives. This is especially important in R&D projects. In the digital age, technology is advancing by leaps and bounds. This may cause companies’ strategic objectives to change and, therefore, the priorities and requirements of R&D projects will have to change as well.
Phase Gate review processes are the perfect opportunity to review topics such as project requirements, priority, budget, resources or delivery dates, and align them with the strategic objectives of the organization.
The Phase Gate process is flexible, being able to adjust to any circumstance or typology of organizations and projects, and thus adapt to your existing business processes. The inclusion over time of agile elements such as the Triple A Process (Agile, Acceleration and Adaptive) ensure the delivery of results in shorter time frames.
Customer involvement in the different phases of the R&D project is crucial. Their feedback will not only define the initial requirements of the project (for example, the usability and operability of the product to be designed), but will also improve the quality of the product and adjust it to the needs of the market as the project progresses.
Customer involvement in the different phases of the R&D project is key
Therefore, its role is essential for R&D projects to offer products and/or services that are easy to use and maintain, as well as to have a greater market acceptance once the launch phase of the project has been reached.
R&D projects are usually large projects that involve multidisciplinary teams, project managers, Product Owners, external partners, etc. Combined with the fact that they may be geographically dispersed across multiple locations and telecommuting, the management of these types of projects can be complex.
However, the Phase Gate process is designed not only to work in this type of situation but also to encourage active collaboration between all parties involved in the project through the review processes of each of the phases. The fact of having people with such a varied disciplinary profile who can objectively review the status and progress of the project from time to time is a guarantee of quality.
R&D project management is one of the cornerstones of many organizations today. And it is precisely because of their importance that it is essential to manage this type of projects efficiently. Resource management, financial management, risk management… There are many aspects to take into account that, if not managed correctly, will cause your R&D projects to fail and not come to fruition.
The Phase Gate methodology will be your best ally to ensure that your organization’s projects are successful and achieve market penetration. And, in order to help you with its management, it is also essential to have a PPM solution like Triskell Software that allows you to handle all aspects related to New Product Development and R&D project management (project prioritization, capacity planning, resource allocation, alignment with strategic objectives, etc.) efficiently and in real-time.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Request a demo of Triskell Software
Want to know how Triskell Software can help you to manage your organization’s R&D projects? Check it out for yourself and request a Triskell demo now.
The Phase Gate process and Agile project management offer distinct approaches, but can also share some common ground. Here’s a breakdown:
The Phase Gate process offers several advantages for R&D projects:
The Phase Gate process isn’t universally applicable. Here’s where it might not be the best fit:
Related Content

Why the CIO needs a PMO approach
Unlock business success: discover why the CIO must embrace a PMO approach! to elevate efficiency and boost productivity.

Lean Budgeting for Agile Portfolios: A Comprehensive Guide
Lean Budgeting: the financial revolution for Agile portfolios. Discover how to streamline project financing and optimize value delivery.

Implementing SAFe with a 7-step roadmap
Do you want to scale Agile at the enterprise level and don’t know where to start? We solve your doubts by explaining the steps to implement SAFe.
Platform
Company
© 2024 Triskell Software. All Rights Reserved.
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Cookies policy
Quality Management and Information Security System Policy

We use technologies such as cookies to store and/or access device information. We do this to improve the browsing experience and to display (non-) personalized advertisements. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique ID's on this site. Not consenting, or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.

Triskell Software, named a Representative Vendor - 2024 Market Guide for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools
Triskell Software has been named a Representative Vendor in 2024 Gartner® Market Guide for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools. Discover how Triskell can assist companies to manage strategies, investments, and outcomes efficiently.