Project Financial Management 101: A Comprehensive Guide for PMOs

In the ever-changing landscape of project management, financial efficiency emerges as an essential pillar for the success of any PMO (Project Management Office).
Throughout this guide, we will dive into the intricacies of project financial management, exploring its meaning, its crucial importance and providing an analytical approach to improve PMO practices.
What is project financial management?
But before we get into the subject, let’s start with the basics: what is project financial management? Project financial management is one of the most important components of project management that goes beyond simply overseeing the accounting for each of the organization’s projects.
In essence, they are a series of processes that enable project managers, financial controllers and the PMO as a whole to plan, manage, monitor and optimize the financial resources allocated to each project. With what objective? To maximize the ROI not only of each project, but of the organization’s project portfolios as a whole.
Why project financials are so important in Project Portfolio Management
Project financial management is at the heart of overall project portfolio management. Efficient planning and use of funds can make the difference between project success and failure. This is because efficient planning and use of funds can make the difference between project success or failure.

STRATEGIC PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
Elevate your PMO above the rest
Discover how PMOs can leverage Triskell capabilities
These are the reasons why project financial management must play a central role in the management of project portfolios:
- Alignment with strategic objectives: financial management ensures that every expenditure is aligned with overall objectives, avoiding investments that do not contribute significantly to the organization’s success. It also facilitates the allocation of resources according to strategic priorities, ensuring that the most critical projects receive adequate attention and funding.
- Financial transparency and visibility: in the complex environment of project portfolio management, lack of visibility and financial transparency can lead to devastating consequences. Financial management provides PMOs clarity on resource allocation and costs associated with each project phase, ultimately enabling informed decision making throughout the project lifecycle.
- Control of budget deviations: one of the biggest risks in project management is the possibility of budget deviations. Financial management acts here as an early prevention system, identifying possible deviations and allowing timely adjustments to keep projects on track.
Financial management provides the PMO with clarity on resource allocation and costs for each project
- Risk mitigation: every project is exposed to a variety of financial risks, from fluctuations in the cost of supplies, inputs or raw materials, to unforeseen changes in project requirements. Thanks to financial management processes, PMOs will not only be able to identify these risks promptly but also formulate strategic plans to mitigate them.
- Resource optimization: every financial decision, no matter how insignificant it may seem, can have an impact on projects. Therefore, financial management should not be limited to controlling expenses but should seek to optimize the use of available resources, identify areas of improvement and opportunities to improve return on investment.
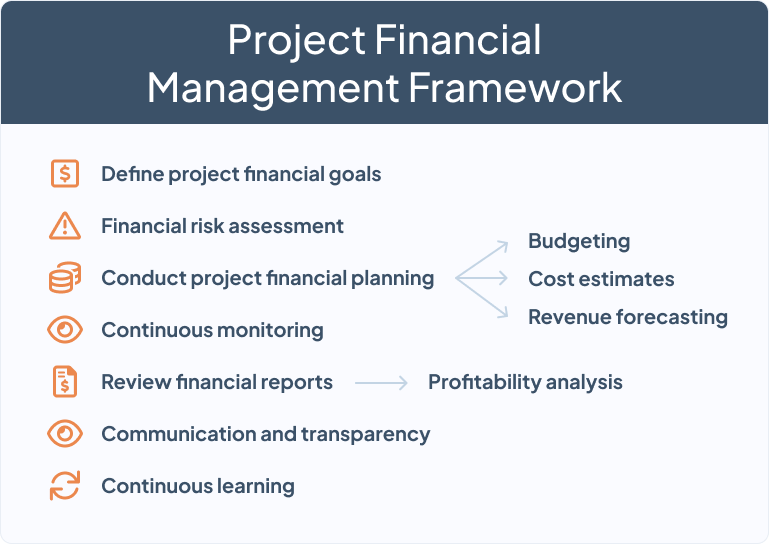
Key elements of project financial management
Project financial management is a multifaceted process that involves the strategic management of several crucial components. This is why PMOs must have an in-depth understanding of each of these elements to establish a solid foundation on which to base the rest of the management processes.
We can distinguish 5 essential components for project financial management:
1. Budgeting
Budgets are the foundation on which project financial management is built. Establishing realistic budgets from the outset provides clear financial guidance and serves as a reference for allocating resources throughout the project and evaluating its performance.
Including both direct and indirect costs ensures a holistic view of the resources required and avoids unpleasant surprises during project execution.
2. Cost estimates
Cost estimation is an essential component preceding the planning phase. It consists of assessing the probable costs associated with each element of the project. This practice, when performed accurately, provides PMOs with a detailed understanding of the financial resources required.
The accuracy of estimates is improved by incorporating accumulated experience from previous projects and best practices in project portfolio management, which contributes to more effective financial planning.
A correct cost estimate provides a detailed understanding of the financial resources required
3. Revenue forecasting
Revenue forecasting is essential to ensure that revenues are aligned with project milestones. This involves, among other things, a carving understanding of:
- Contractual terms with customers and/or external suppliers.
- Terms of payment.
- Synchronization of invoices with project achievements.
Accurate revenue forecasting contributes to the efficient management of cash flows and maximization of return on investment.
4. Financial reporting
Financial reporting plays a crucial role in communication and informed decision making. These reports provide a detailed view of the project’s financial status, highlighting areas of success and challenges. They should include profitability analysis, budget variance tracking and future projections.
The use of visual tools and executive summaries facilitate understanding even for those without in-depth financial knowledge, thus fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
5. Profitability analysis
Profitability analysis goes beyond mere accounting and becomes an ongoing assessment of the project’s financial performance. It involves measuring ROI, evaluating profit margins and identifying areas of improvement.
This component allows PMOs to learn from experience, adjust future strategies and maximize financial efficiency in subsequent projects.
Best practices to improve project financial management
Continuous improvement in project financial management is essential to adapt to changes in the business environment and maximize efficiency in project execution. Here we present a series of tips and best practices that go beyond day-to-day management and focus on long-term strategies to elevate financial excellence in project management.
1. Detailed project planning
Detailed planning is the first step in optimizing project financial management. Detailed planning is the first step in optimizing project financial management. This involves preparing a comprehensive financial plan at the outset of the project. Management teams should work closely with financial controllers to identify all potential costs, from the most obvious to those that may arise unexpectedly.
As you can see, detailed planning helps set realistic financial expectations and serves as a framework for evaluating performance at each stage of each project’s life cycle.
2. Continuous monitoring
Continuous monitoring is an essential practice that goes beyond mere observation of project performance. It is based on the identification and tracking by the PMO of the relevant KPIs for each project. These indicators should not be limited only to financial aspects, but should cover other critical aspects that directly impact project performance, such as operational efficiency or customer satisfaction.
In addition to establishing relevant metrics and KPIs, PMOs should leverage predictive analytics to anticipate potential financial risks before they arise. Using advanced algorithms and statistical models, you can examine historical patterns and external factors to forecast future trends, allowing you to address potential problems before they significantly affect projects.
3. Financial risk assessment
Improving financial management involves a proactive assessment of financial risks. Identifying potential risks, assessing their impact and developing strategies to mitigate them are fundamental steps. This assessment is not only limited to the planning phase but should be a continuous process throughout the project.
Risk assessment should be performed at all stages of the project
The ability to anticipate and proactively address financial risks allows Project Management offices to adapt to unexpected changes and minimize the impact on the financial health of the project.
4. Communication and transparency
Effective financial management requires effective communication in all directions. Maintaining transparent communication about the financial status of projects will not only strengthen trust with stakeholders, but also foster an environment in which teams can identify and address challenges collaboratively.
Scheduling recurring meetings, clear financial reporting and open communication channels are crucial to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the financial aspects of projects.
5. Continuous learning
Project financial management cannot be understood without learning and continuous improvement. Analyzing past projects is essential to identify areas for improvement and refine financial practices. Post-project feedback, performance reviews and incorporating lessons learned into future projects are key aspects of this process.
Continuous learning ensures that PMOs evolve and constantly improve their ability to address financial challenges and optimize performance in each new initiative.
Challenges PMOs face with project financial management and how to overcome them
Project financial management poses unique challenges for PMOs, and addressing them effectively is critical to long-term success. Here we explore five key challenges and strategies for overcoming them:
1. Monitoring non-relevant KPIs
Tracking non-relevant KPIs can lead to a distorted perception of the financial results of projects. There is a risk of focusing on metrics that do not accurately reflect their real impact.
How to address this challenge?
- The key is to identify and constantly adjust the KPIs so that they are aligned with the project objectives.
- To do this, you should conduct regular assessments to ensure that the chosen KPIs provide an accurate and complete picture of the project’s financial performance.
- Being flexible in adapting KPIs as projects evolve is essential for monitoring to deliver value throughout the project lifecycle.
KPIs must be constantly adjusted so that they are aligned with project objectives
2. Cost variability
Cost variability can arise due to changes in raw material prices, market fluctuations or unforeseen events during project execution, which can significantly affect the initial budget.
How to address this challenge?
- By implementing a proactive cost management approach, including provisions for possible variations.
- By constantly reviewing cost estimates and creating a reserve fund in budgets to deal with these unexpected changes.
3. Changes in project requirements
Changes in project requirements are, in many cases, unavoidable, and can impact both deadlines and previously established costs.
How to address this challenge?
- By implementing a robust change management system that assesses the financial impact of any adjustments to project requirements.
- By fostering effective communication with all stakeholders to understand the scope of the changes and make informed decisions on how to manage resources and budgets accordingly.
4. Lack of data consistency
Inconsistency in financial data can arise due to the use of multiple applications, making it difficult to generate accurate reports and make decisions based on reliable data.
How to address this challenge?
- By implementing a project portfolio management platform that can be integrated with the systems you use today for project management.
- Such a centralized solution would ensure consistency of financial data and facilitate accurate and reliable reporting.
A PPM software will provide you with consistent financial data and accurate, authoritative reports
5. Inefficient risk assessment processes
Ineffective risk management can result in a lack of anticipation and preparation for unexpected events, negatively impacting the financial health of projects.
How to address this challenge?
- By developing a comprehensive risk assessment process to identify, evaluate and mitigate financial risks.
- By encouraging close collaboration between project teams and finance managers.
- By regularly reviewing and updating risk assessment and mitigation strategies so that the PMO is prepared to address any financial eventuality.
Project financial features that a PPM software must include
The choice of project portfolio management software is a critical step for PMOs, and specific functionalities related to financial management play a crucial role. Here are the essential features that a PPM (Project Portfolio Management) software must offer to ensure effective and transparent financial management.
- Budget vs. planned cost and actual cost: having an overview of the financial status of projects at all times is essential for informed decision making. Any PPM software should include functionalities that allow comparing the initial budget with the planned and actual costs of the project. This gives PMOs a detailed view of how costs evolve over time, identifying possible deviations and facilitating timely adjustments in financial planning.
- Scenario simulation: the ability to simulate future scenarios is essential for strategic planning. A comprehensive PPM software should offer tools that allow PMOs to explore different scenarios and assess their financial impact. This will provide a clearer view of possible variations in costs, revenues and other financial aspects, allowing for more informed decision making.
- Strategic financing: an advanced PPM software must include functionalities that facilitate strategic financing, allowing PMOs to optimize their financial resources. This implies the ability to evaluate different sources of financing, analyze their impact on the project and make decisions that maximize the return on investment.
- CAPEX & OPEX: The ability to distinguish between capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operating expenditures (OPEX) is crucial for accurate financial management. A PPM software must offer functionalities that allow a clear classification of these expenses and an accurate tracking of their impact on the project budget.
- Customizable financial reports: A PPM software should offer functionalities that allow the creation of customizable reports to suit the specific needs of the PMO and stakeholders. Reports should cover aspects such as project financial status, cost analysis, projections and budget comparisons.
- Integration with external accounting and financial systems: Interoperability is key in financial management. Effective PPM software must integrate seamlessly with external accounting and financial systems used by the organization. This facilitates the transfer of financial data efficiently, avoiding duplication of effort and ensuring consistency of information.
All these functionalities can be found in Triskell Software’s PPM platform.
Conclusion
To summarize, project financial management is not simply an accounting task; it is an essential strategy for the continued viability and growth of organizations. Adopting an analytical approach and using the right software tools can make the difference between failure and triumph.
By addressing challenges with practical solutions, PMOs can maximize financial efficiency and ensure successful project delivery. Ultimately, project financial management is a discipline in its own right, where the integration of analytical insights and advanced tools translates into sustainable success in the complex world of project management.
Request a demo of Triskell Software
Triskell meets all the requirements for your organization’s PMO to take a step forward in aligning your project portfolio with strategic planning.
Related Content

10 types of Project Management Offices (PMO): structure, purpose and how to choose the right one
Learn about different PMO types, their governance levels, and which one is the best fit for your company’s project management needs.

How to create a project budget: methods and techniques for effective project budgeting
Learn how to create a project budget with this detailed guide. Discover essential methods and techniques for effective project budgeting in PPM.

20 strategic planning models and tools for medium and large companies
Looking for the best strategic planning frameworks? This guide covers 20 proven models to enhance decision-making and business growth.
FAQs about Project Financial Management
How can a PMO improve financial forecasting accuracy in project management?
Improving financial forecasting accuracy involves utilizing historical data from previous projects, implementing predictive analytics, and regularly updating financial models based on real-time data.
Additionally, fostering close collaboration between project managers, financial controllers, and stakeholders helps ensure that forecasts align with current project conditions and market trends.
What are the long-term benefits of implementing strong project financial management practices?
Implementing strong project financial management practices leads to several long-term benefits, including enhanced financial transparency, better alignment of projects with strategic objectives, improved risk management, and optimized resource utilization.
Over time, these practices contribute to higher project success rates, increased ROI, and overall organizational growth and sustainability.
What role does technology play in project financial management?
Technology plays a critical role in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of project financial management. Project Portfolio Management (PPM) software, for instance, offers features like budget tracking, scenario simulations, CAPEX & OPEX differentiation, and integration with accounting systems.
These tools help PMOs manage finances more effectively by providing real-time insights, automating financial processes, and enabling better decision-making.