Lean Budgeting for Agile Portfolios: A Comprehensive Guide

Tired of spending hours and hours managing project and product portfolio budgets in the usual Excel spreadsheets? We know how you feel. Not only is this a frustrating task, but in today’s dynamic business landscape, this method of budget management has become obsolete.
And you, who have been managing project finances in the same way for years and years, may be wondering: is there another way? Is there a flexible, value-driven approach to budget management that is adapted to the frenetic pace of your organization and the market? In this post, you’ll discover what Lean Budgeting is, and how its approach based on Lean Portfolio Management empowers teams, fosters agility and drives results.
Sounds interesting, right? If you want to transform your organization’s portfolio allocation and budget management processes, keep reading.
What is Lean Budgeting?
You know what it takes to manage projects and programs with Agile methodologies. These are initiatives in which changes in requirements and scope are the norm. And their focus on satisfying customer needs makes it necessary for teams to deliver ‘tangible’ value in the shortest possible time.
Given this reality, a new approach to allocating and managing product budgets is needed. It is no longer enough to allocate a fixed budget at the beginning of each initiative, which will hardly vary. Product lifecycles are more dynamic than ever because customers and users are present in the process. And, based on their feedback, the scope may change, or functionality may need to be added or modified to ensure that the customer is fully satisfied with the final product or service.
Lean Budgeting emphasizes the importance of breaking budgets into smaller increments
Project lifecycles are now living, dynamic workflows. And this is precisely the essence of Lean Budgeting. It is an approach to Budget Management that seeks to maximize the real value delivered to customers by eliminating wasteful spending. How? By releasing budget items in smaller parts (also called Horizon in SAFe) along the organization’s value streams. This allows adjustments to be made based on feedback and thus keeps all teams focused on developing the functionality that really delivers value.
Benefits of Lean Budgeting
Lean Budgeting, therefore, is not just about adjusting the allocation of funds in product portfolios. It is a radical change in the way budgets are managed that enables teams to make informed decisions and optimize results in fast-paced work environments.
These are the main benefits of Lean Budgeting:
- Increased agility: your organization will be able to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands.
- Less waste: you will use funds more efficiently and minimize unnecessary expenses and cost overruns.
- Focus on value delivery: Lean Budgeting focuses on the organization’s value streams, so investments will be allocated to those activities that generate the greatest impact.
- Team empowerment: your teams will have more autonomy to make decisions and optimize the results of the products and services they are working on.
- Sustainable innovation: Lean Budgeting fosters a culture of continuous improvement that will drive your long-term research and R&D efforts.

AGILE PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
Make SAFe implementation a reality with Triskell
Learn more about Triskell’s Agile PPM solution
Key components of Lean Budgeting
To master Lean Budgeting, it is crucial to become familiar with its components. These interconnected elements form the basis of agile and effective financial management, adapted to the needs of today’s market.
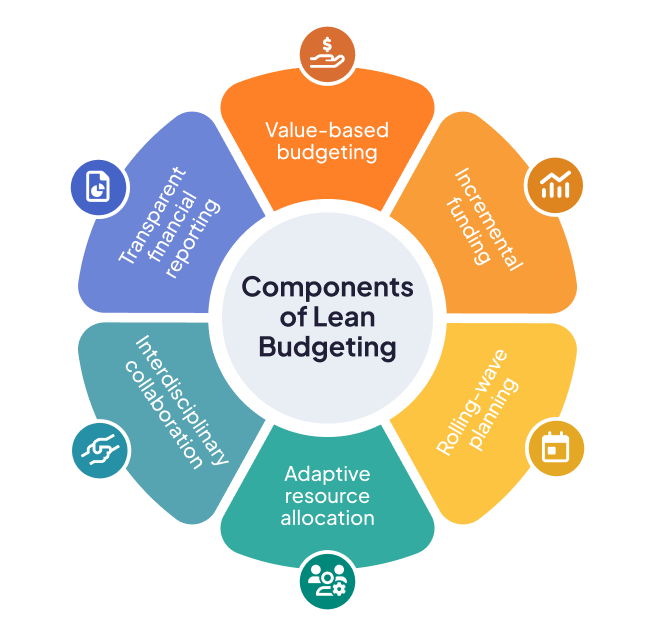
Value-based budgeting
This is the backbone of the entire Lean Budgeting process. It consists of evaluating each expense carefully to ensure that each initiative or task contributes to delivering value to customers. The goal? To ensure that you prioritize those products or features that will have a positive impact on business results and, above all, on the experience and satisfaction of your customers.
To allocate budgets based on value, here are 3 tips:
- Map your organization’s value streams to identify and eliminate activities that don’t add value, so you can focus on the processes that actually deliver benefit.
- Use prioritization techniques, such as cost-benefit analysis or scoring models, to help product teams evaluate initiatives based on the value they can deliver.
- Regularly survey customers to ensure that your budget allocation decisions are aligned with their changing needs and expectations.
Incremental funding
Lean Budgeting adopts an incremental funding approach, in which funds are released in phases as projects and deliverables progress. As you can see, this is a totally different approach from the traditional allocation of funds at the beginning of each initiative, and it works like this:
- You must assign a budget to each phase of the project, product and even each functionality according to its scope and deliverables.
- Funding decisions should be made based on the fulfillment of milestones and after demonstrating with data the value of the project, product or functionality to be worked on.
- You should track the progress of each initiative so that you can make adjustments in the allocation of funds when necessary.
This incremental approach will bring you many benefits when managing the budgets of your product portfolios. For example:
- You minimize the risk of cost overruns or project failures by releasing funds as each initiative progresses.
- Your organization gains flexibility to adjust funding allocations to changing priorities or emerging needs.
Boost efficiency and deliver value faster
Request a demo today and discover how Triskell fosters collaboration across teams and facilitates faster value delivery within SAFe framework.
Adaptive Resource allocation
Another differentiating element of Lean Budgeting is the way in which resources are allocated. Instead of being planned at the beginning and with little change throughout the product life cycle, a flexible and adaptive approach to resource allocation is adopted.
Imagine this scenario: your team is working on a new product. And, after 2 months of work, you discover a new market opportunity that means the scope of that new product needs to change, requiring additional resources. With this adaptive approach to resource allocation, you can request and receive the help they need without compromising your organization’s performance. It will also enable you to:
- React quickly to changing project requirements or emerging opportunities.
- Transfer resources to the areas where they will have the greatest impact, ensuring that they are not underutilized or wasted.
Lean Budgeting enables organizations to adapt to changing needs and priorities
Rolling-wave planning
Many organizations, when it comes to budgeting, adopt an approach whereby the budget is planned for the entire year, without changing throughout that time. With Lean Budgeting, on the other hand, you have to plan the budget in short cycles in order to be able to:
- Make adjustments as more information becomes available or priorities change.
- Focus on the most urgent tasks or functionalities without losing sight of the overall scope and vision of the product or service.
- Identify and fix problems in advance before they escalate.
Interdisciplinary collaboration
Based on what we have explained so far, you probably think that Lean Budgeting is just a new way of managing an organization’s finances. But it is much more than that. Adopting this new approach will mean leading a cultural change in which interdisciplinary collaboration must be key.
If there are silos in your organization, budget decisions are made without considering the views of all the teams that will be directly or indirectly involved in the work. In contrast, if you put Lean Budgeting processes in place, you will help foster cross-functional collaboration throughout the entire budget allocation process.
With Lean Budgeting, all stakeholders in your organization (product team, marketing, sales, etc.) will have a joint view of the budget and its implications for the work they have to do. In this way, teams will be jointly accountable for the budget, and you will foster a sense of shared responsibility for achieving the overall financial and business objectives.
Lean Budgeting is not just a new way of managing budgets, it is a cultural change
Transparent financial reporting
In line with the previous point, transparency is fundamental in the Lean Budgeting process. Everyone, from executives to product team members, must have access to real-time financial information.
To do this, you must schedule financial reports to inform periodically each stakeholder on the health of the product portfolios. These reports should be easily understandable, highlight strengths and areas for improvement, and be accompanied by visual aids to make them easier to understand.
Furthermore, you must have communication channels through which budget decisions can be consulted and allow stakeholders to provide their comments and opinions and thus facilitate a common understanding.
Continuous improvement
Lastly, Lean Budgeting is not an immovable set of rules and processes. As with Lean methodology, it is subject to a strict continuous improvement process in which teams must regularly evaluate and optimize their budgeting processes, and thus look for ways to improve efficiency and continuous value delivery.
You can drive continuous improvement processes in your organization in a variety of ways:
- Learning from past projects, identifying areas for improvement to avoid repeating mistakes and optimizing the focus of future initiatives.
- Explore new formulas and tools for budget allocation to keep your teams at the forefront of best practices and maximize their impact.
- Put customer feedback at the center of all your Lean Budgeting processes so that Budget Management is always aligned with their needs and expectations.
Lean Budgeting is a process of continuous improvement that requires constant requires constant collaboration and adaptation
The importance of establishing ‘Lean Budget Guardrails’
As you can see, Lean Budgeting is a financial management process that is much more flexible than traditional financing methods. However, this flexibility does not imply that limits and guidelines should not be established for the process to be effective.
These guidelines, also known in the SAFe methodology as Lean Budgeting Guardrails, will be your reference to avoid misuse or misinterpretation of Lean Budgeting and Lean Portfolio Management principles.
Objectives of Lean Budgeting Guardrails
Lean Budgeting Guardrails do not serve a single particular purpose, but have multiple objectives:
- Help ensure that budget decisions are focused on delivering value to customers and avoid wasting resources on activities that lack impact.
- Promote transparency throughout the budget process, and help all stakeholders understand the rationale for decisions and have access to relevant financial information.
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities within the budget process.
- Help avoid cost overruns by setting spending limits and clear procedures for requesting additional funds.
Types of Lean Budgeting Guardrails
Therefore, Lean Budget Guardrails are guidelines that will help you stay on track and avoid potential financial pitfalls along the way. We can classify them into 4 categories:
- Target investments by Horizon: you should diversify investments between short-term needs, new developments, and long-term opportunities. This will ensure that your product portfolios remain innovative over time.
- Balance capacity: don’t just focus on new features. Allocate resources for maintenance and technical improvements as well. This will make your operation efficient.
- Approval of the most relevant initiatives: Major decisions require special attention. While smaller projects can be approved following the Value Stream’s own governance processes to which they belong, large initiatives must be approved by the organization’s executives to ensure that they align with the strategy and minimize risks.
- Continuous engagement of Business Owners: you must involve the company’s leaders in all budget allocation processes. This will help prioritize what matters most and keep everyone focused on delivering value.

Strategies for implementing Lean Budgeting in your Agile Portfolios
To implement Lean Budgeting effectively in your Agile portfolios, it is essential to follow some best practices that will ensure a smooth and successful transition. Here I show you the two most important ones.
Changing the traditional mindset
A change of approach to allocating and managing budgets as proposed in Lean Budgeting will require a radical change of mindset in your teams. This can be extremely difficult for organizations used to working with the same processes for years and a silo mentality.
To address this challenge, I recommend that you follow these best practices:
- Foster a culture of continuous value delivery to customers in which budget decisions with strategic objectives.
- Promote open discussions about budgeting practices, address issues and encourage the participation of all stakeholders.
- Provides training and support to help employees understand and adopt the principles of Lean Budgeting.
Establish clear value metrics
In Lean Budgeting, accurately measuring and assessing the value of projects and initiatives is critical to making informed budgeting decisions. However, defining and quantifying that value can be complicated, especially when it comes to intangible benefits.
To help you define these performance indicators, try these tips:
- Establish clear and specific criteria (both quantitative and qualitative) to assess the value delivered by each initiative.
- Involve all stakeholders (teams, executives, customers, etc.) in the value assessment process to get each stakeholder’s point of view.
- Set KPIs and metrics to measure and analyze the impact of each product portfolio.
WHITE PAPER
Agile Portfolio Management – Agility by delivering changes as business as usual
Tools and techniques to support your Lean Budgeting framework
For Lean Budgeting to be effective, it is essential to have the right tools and techniques to facilitate the process and ensure its success. These are just some of the ones you need to get the most out of this process.
- Value stream mapping: this technique will help you identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline processes and, ultimately, optimize the allocation of funds.
- Forecasting tools: these solutions allow you to make forecasts and budget adjustments as new information becomes available. They are ideal for adjusting budgets in real time according to the needs of each initiative.
- Collaborative communication platforms: tools such as Teams, Slack or Triskell Software will help you foster collaboration and communication between teams, stakeholders and finance departments. This way, everyone will be aligned with the budget decisions being made.
- PPM software: Project Portfolio Management software can help you streamline your Lean Budgeting processes by facilitating value stream financing, Scenario Simulation, and real-time cost tracking.

Streamlining Lean Budgeting with Triskell Software
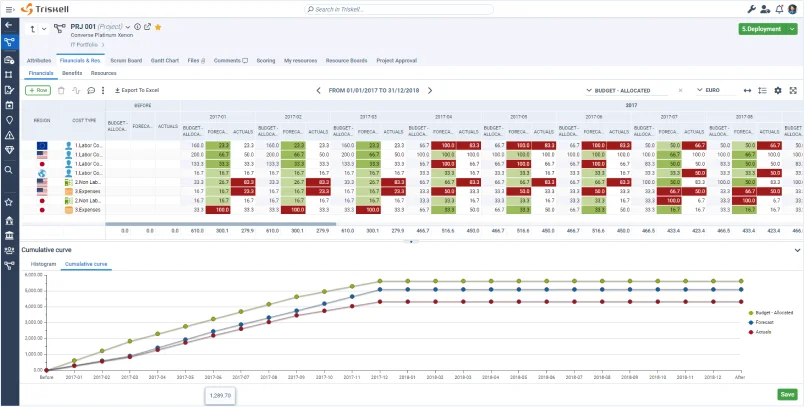
Triskell Software is a comprehensive platform for project, budget and portfolio management that facilitates planning, real-time financial tracking and alignment with strategic objectives. Triskell offers a wide range of functionalities with which you can streamline and significantly improve your Lean Budgeting process. For example:
- Centralized financial management: Triskell is much more than a project and program management tool. It is a platform from which you can manage budgets, financial data and all documentation related to the project and product portfolios of any corporation.
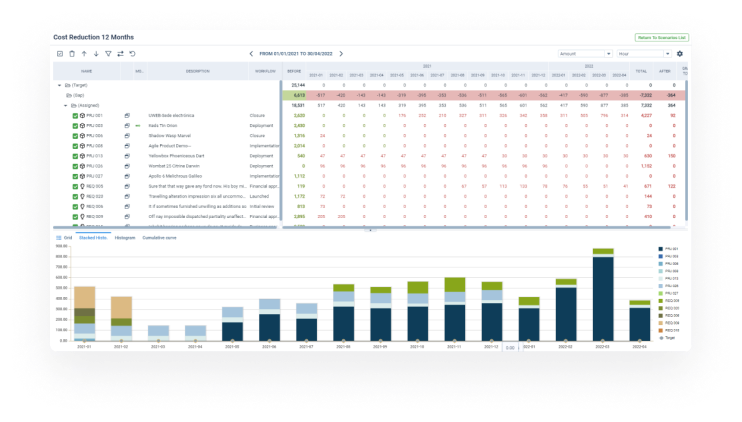
- Real-time budget reports: you can track budget allocations and expenditures in real time. It helps you to detect budget deviations in advance and take corrective action quickly.
- Scenario planning and simulation: thanks to this functionality, you can model different financial outcomes, anticipate future budget needs, and detect problems in advance.
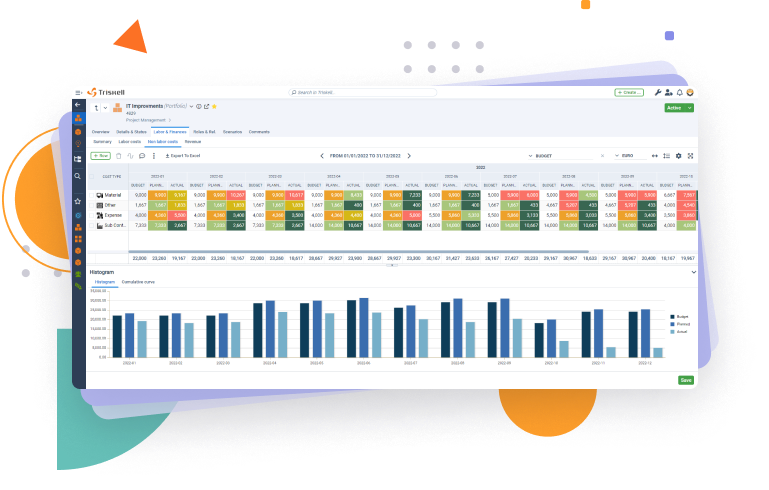
- Alignment with strategic objectives: Triskell will help you focus on delivering value as you can align your Financial Management processes with the overall objectives of the organization.
- Workflow automation: automate with a few clicks tasks such as approving, reviewing or tracking budgets for each project, program or portfolio.
- Audit trail: Triskell keeps a comprehensive audit trail of all budget changes. It is a platform with which you can comply with regulatory requirements and your organization’s internal or external auditing standards.
- Integrations with other systems: you will be able to integrate Triskell with other applications you already use internally in your company, such as ERPs, accounting systems, Jira or CRM.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Get stories like this in your inbox
Conclusion
In short, Lean Budgeting is not just a simple budgeting approach, but a cultural shift that empowers teams, fosters agility and drives value creation. By adopting its core principles and overcoming its challenges, organizations can adopt a dynamic approach to financial management that keeps them ahead of the curve in today’s frenetic business environment.
So, ditch the Excel spreadsheets and project-based budgeting. Embrace the flexibility of Lean Budgeting and make your budgets work for you, not the other way around.
Boost efficiency and deliver value faster
Request a demo today and discover how Triskell fosters collaboration across teams and facilitates faster value delivery within SAFe framework.
Related Content

10 types of Project Management Offices (PMO): structure, purpose and how to choose the right one
Learn about different PMO types, their governance levels, and which one is the best fit for your company’s project management needs.

How to create a project budget: methods and techniques for effective project budgeting
Learn how to create a project budget with this detailed guide. Discover essential methods and techniques for effective project budgeting in PPM.

20 strategic planning models and tools for medium and large companies
Looking for the best strategic planning frameworks? This guide covers 20 proven models to enhance decision-making and business growth.
FAQs about Lean Budgeting
How does Lean Budgeting ensure accountability and prevent overspending?
Lean Budgeting employs a set of guidelines known as Lean Budget Guardrails to maintain accountability and control over spending.
These guardrails help ensure that budget decisions are focused on delivering value, maintain transparency, clearly define roles and responsibilities, and set limits to prevent overspending.
Regular financial reporting and continuous engagement with business owners also play a critical role in monitoring and managing expenditures effectively, reducing the risk of cost overruns.
Is Lean Budgeting suitable for all types of organizations or projects?
While Lean Budgeting is particularly beneficial for organizations that operate in dynamic and fast-paced environments, such as those following Agile methodologies, it can be adapted to various types of organizations and projects.
The key is to ensure that the principles of Lean Budgeting, such as value-based funding, incremental allocation, and continuous improvement, align with the organization’s goals and project requirements.
However, organizations with rigid, highly regulated environments may need to adapt Lean Budgeting principles carefully to fit their specific constraints.
What role do tools and software play in implementing Lean Budgeting effectively?
Tools and software are essential in effectively implementing Lean Budgeting, as they facilitate key processes such as value stream mapping, forecasting, real-time financial tracking, and collaboration across teams.
For example, Project Portfolio Management (PPM) software can help streamline budget management by automating workflows, simulating financial scenarios, and ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
Collaborative platforms, such as Triskell Software, further enhance the effectiveness of Lean Budgeting by providing real-time budget reports, audit trails, and integrations with other enterprise systems.

