The ultimate PMO guide: roles, responsibilities and best practices for successful implementation

Today, PMOs (Project Management Offices) are an indispensable element in complex organizations that need to manage multiple project portfolios and align results with their strategic objectives. Thanks to a PMO, project success rates can be improved, processes can be standardized and consistency between projects can be ensured, all of which are key elements for any organization to achieve its goals.
In this article, we will explain in detail what a PMO is, its roles and responsibilities, and the steps to take to implement one in your organization. Do you want to implement a PMO and don’t know where to start? Then read on.
What is a PMO? Definition and scope
PMO is an acronym for Project Management Office. It is a department responsible for defining and enforcing project management standards within a company. Its primary function is to provide governance, support, and guidance to ensure that all projects adhere to best practices, align with business objectives, and deliver value.

PMO MANAGEMENT
Streamline your PMO operations
See how Triskell enables PMOs to optimize processes, streamline workflows, and deliver projects efficiently.
The scope of a PMO can vary depending on several factors, such as the size and structure of the organization or the complexity of the projects. Some PMOs focus on overseeing the management of complex project portfolios, offering high-level governance and monitoring the resources across all projects. Others, however, may take on a more active role in project execution, providing direct support and resources to the projects.
Each company is unique, which means that each PMO can have a very different approach and level of involvement. Even so, we can say that, broadly speaking, there are 3 types of PMO:
- Supportive PMO: it focuses on offering guidance, providing templates, advice on best practices and training.
- Directive PMO: it actively involves in project management, taking direct control of the projects and assigning dedicated Project Managers to work exclusively on the projects.
- Controlling PMO: it represents a middle ground between the two above, offering guidance and setting standards for project management while also overseeing project execution.

PMO roles and responsibilities
Certainly, regardless of its type, a PMO is not composed of just one person but includes multiple roles, each with a well-defined list of responsibilities and functions.
Below are the key roles typically found within a PMO:
1. PMO Director
The PMO Director is the strategic leader of the PMO. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Aligning the PMO’s objectives with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Ensuring the PMO delivers value to all projects by making high-level decisions.
- Collaborating closely with the organization’s executives to define the scope, priorities, and oversight of the PMO’s activities.
2. PMO Manager
The PMO Manager oversees the daily operations of the PMO, ensuring the standards and processes defined by the PMO Director are implemented. Their responsibilities include:
- Managing the PMO staff.
- Coordinating project activities.
- Ensuring PMO tools and methodologies are effectively utilized.
- Monitoring project reporting.
- Supporting risk management efforts.
- Aligning project activities with strategic objectives.
3. Portfolio Manager
The Portfolio Manager is responsible for selecting and prioritizing projects that align with the organization’s strategy. This role involves:
- Evaluating project proposals.
- Monitoring the progress of projects within their portfolio.
- Optimizing the allocation of project resources.
- Balancing project benefits, risks, and costs.
- Providing executives with a clear overview of portfolio performance.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Get stories like this in your inbox
4. Project Manager
While Project Managers are directly responsible for managing project execution, they play a critical role within the PMO by ensuring projects adhere to established standards. Their key responsibilities include:
- Planning, executing, and closing projects.
- Coordinating team members.
- Managing project scope, timelines, and budgets.
- Reporting progress, challenges, and outcomes.
5. PMO analyst
Lastly, the PMO Analyst focuses on data collection and reporting. Their responsibilities include:
- Providing performance insights to stakeholders in an accessible format.
- Tracking project metrics.
- Identifying trends and issues requiring attention.
PMO vs project manager: a comparison table
Aspect |
PMO |
Project Manager |
|---|---|---|
|
Scope |
Oversees and manages multiple projects at the organizational level to align with strategic goals. |
Focuses on managing individual projects. |
|
Focus |
Governance and strategy. |
Project execution and delivery. |
|
Responsibilities |
|
|
|
Decision authority |
Defines policies and guidelines but does not make operational decisions for specific projects. |
Makes decisions regarding activities, teams, and resources allocated to the project. |
|
Risk Management |
Identifies common risks across all projects and establishes organizational mitigation strategies. |
Identifies, monitors, and mitigates risks specific to their project. |
|
Communication |
Identifies common risks across all projects and establishes organizational mitigation strategies. |
Identifies, monitors, and mitigates risks specific to their project. |
|
Key skills |
|
|
|
Reporting to |
Reports to senior management and the company’s executive committee. |
Reports to the project sponsor, PMO, or project steering committee. |
PMO tasks and processes
Within the PMO, all roles must work together to ensure project success and alignment with organizational objectives. To achieve this, the PMO must manage a series of processes and tasks that not only guarantee the alignment of projects with the organization’s strategy but also optimize resource utilization, mitigate risks, and foster team collaboration.
Here is a comprehensive list of PMO processes and tasks:
- Project prioritization: evaluate and determine which initiatives should be prioritized based on their strategic importance and impact on organizational objectives.
- Project initiation: define project objectives, scope, and key deliverables from the outset to ensure alignment with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Resource allocation: efficiently distribute project resources (personnel, tools, budget, etc.) to ensure smooth project progress.
- Timeline definition: develop a clear schedule with key milestones and realistic deadlines to guide timely project delivery.
- Task management: Organize and oversee team activities, ensuring everyone knows what to do and by when to keep the projects on track.
- Communications management: facilitate communication among teams, leaders, and stakeholders to ensure everyone is aligned and informed.
- Change management: implement strategies to handle modifications (e.g., scope adjustments or resource reallocations) with minimal and controlled impact on the projects.
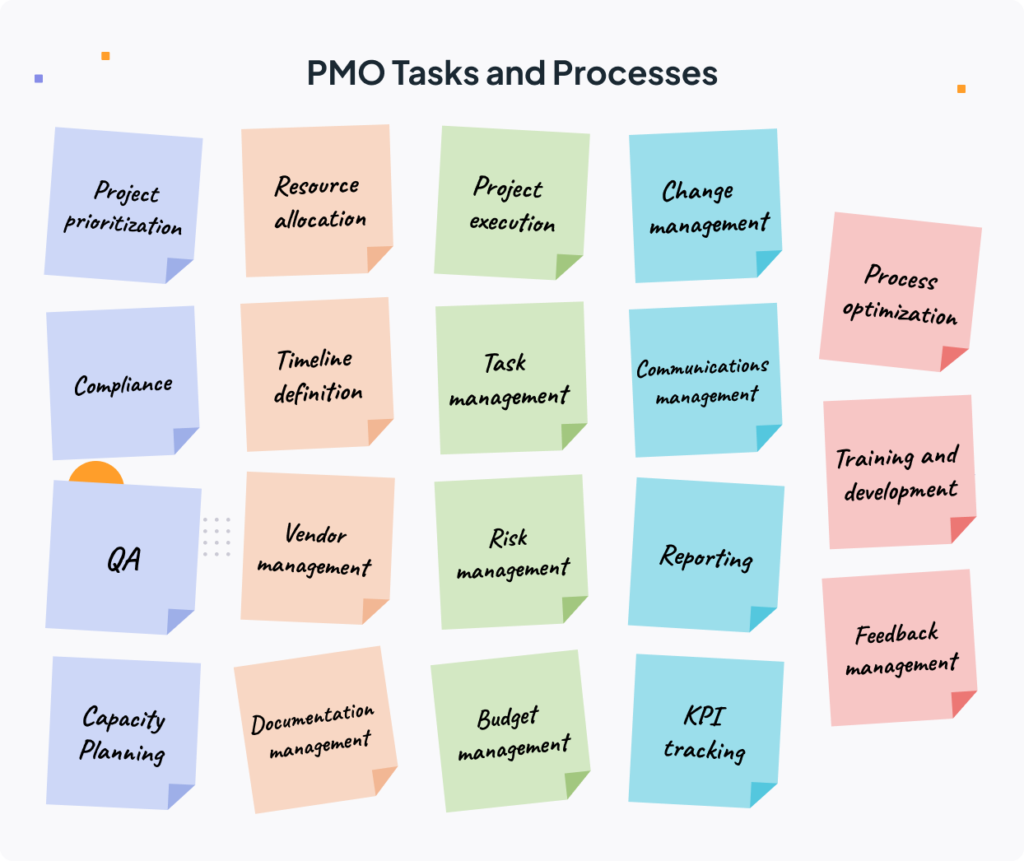
- Documentation management: ensure all project-related information is well-organized, updated, and readily accessible for consultation at any time.
- Risk management: anticipate potential issues, assess their impact, and define actions to mitigate or prevent them.
- Compliance: ensure projects adhere to current regulations, internal policies, and organizational guidelines.
- Quality assurance (QA): guarantee that projects and their deliverables meet the quality standards defined from the outset.
- Reporting: prepare clear, easy-to-understand reports to keep stakeholders informed about the performance of the organization’s project portfolio.
- KPI monitoring: define key performance indicators for each project and monitor them to determine whether adjustments are needed to stay on track.
- Capacity planning: ensure the organization has sufficient resources to handle both the current project backlog and future demand, preventing team overload.
- Budget management: track project expenditures rigorously to ensure they remain within the agreed budgets.
- Vendor and contractor management: coordinate the involvement of external parties in projects, ensuring they deliver as agreed in terms of time and quality.
- Process optimization: continuously review and improve project management processes to enhance efficiency and outcomes.
- Training and development: equip teams with the tools and knowledge needed to address project challenges effectively.
- Feedback management: collect and analyze stakeholder feedback to identify improvement areas and apply lessons learned to future projects.
Your PMO’s next big step starts right here
Request a demo to see how Triskell Software can help your PMO enhance efficiency, deliver projects on time, and align with business goals.
Benefits of a PMO for medium and large companies
Despite its intricate dynamics and processes, implementing a PMO offers countless benefits, especially for companies facing increasing volumes and complexity in project management.
Here are the key benefits of PMOs for medium and large enterprises:
- Higher project success rates: the structured approach provided by the PMO enhances the likelihood of project success.
- Improved operational efficiency: by standardizing processes within the organization, the PMO boosts overall team productivity, reduces redundancies, and minimizes waste.
- Greater visibility and control: PMOs provide executives, teams, and project managers with a clear view of the status of projects, programs, and portfolios across the organization.
- Better decision-making: this enhanced visibility enables more efficient decision-making in areas such as project prioritization, risk management, and resource allocation.
- Cost reduction: the PMO helps organizations lower costs by eliminating project inefficiencies and ensuring budgets are managed effectively.

A 7-step PMO implementation process
While the benefits of a PMO are countless, its implementation is not exactly a smooth ride. You will encounter many obstacles along the way, and to tackle them you will need a clear and structured approach to succeed.
We at Triskell Software recommend that you follow this 7-step process so that your organization can successfully implement a PMO.
1. Define the PMO’s purpose and scope
The first thing to do is to answer the following question: what is the objective to be achieved? If the answer is not clear, the implementation of a PMO in your organization will hardly be successful.
In this phase, you must do the following:
- Define the needs and requirements: you need to identify and analyze the pain points you want to address. Are projects not being completed on time? Are resources being wasted? Is there no alignment with strategic objectives? Talk to the different stakeholders to investigate their needs and lay the groundwork for their support of the PMO.
- Establish the scope: after talking to all stakeholders, you will have more than enough elements to define the scope and level of authority of the PMO.
- Draft a PMO charter: this document should reflect the PMO’s purpose, responsibilities and reporting structure. It should also include the strategic objectives, scope and success indicators. Additionally, it should define who makes decisions and how accountability will be managed.

2. Secure executive sponsorship
Gaining support from senior management is critical to the successful implementation of a PMO. Their backing not only reinforces the PMO’s credibility but also ensures access to the resources needed to staff and operate it effectively.
- Identify key stakeholders: the success of the PMO depends not only on the support of senior management. Obtain the support of the heads of the departments most affected by project results (IT, Marketing, Sales, etc.).
- Communicate the vision: clearly articulate the value the PMO will bring to the organization. Use data to demonstrate how it will improve project outcomes and support strategic objectives, thereby securing stakeholder buy-in.
- Secure the budget and resources: make sure you secure the appropriate funding for the PMO. This will allow you to equip it with the necessary personnel and tools to ensure optimal performance.
3. Establish the PMO team
Once you have the sponsors and resources for the PMO, you need to define the team that will comprise it. Some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Hire or assign staff: at a minimum, the PMO should have a PMO Manager, a Portfolio Manager, and a PMO Analyst. Depending on the size and needs of the organization, additional Project Managers and Portfolio Managers may be required. It is recommended to select professionals with experience in Project Management, strong organizational skills, and strategic thinking capabilities.
- Define roles and responsibilities: assign specific tasks and responsibilities to each role to avoid duplication of efforts and ensure accountability. Additionally, define performance metrics for each role so team members can see how their contributions align with the success of the PMO and the organization as a whole.
- Provide training and development: invest in training to equip the PMO team with the foundational skills necessary to manage projects effectively. This training may include courses on project management methodologies, communication techniques, or the use of project management and PPM tools.
4. Develop PMO standards and processes
The PMO should analyze the organization’s existing processes and standardize them to ensure consistency across projects and improve efficiency.
- Establish governance processes: set up governance processes for the PMO, including approval workflows, decision-making hierarchies, and reporting chains. Clear governance structures help align everyone and ensure cohesive project management practices.
- Standardize project management methodologies: define and standardize the methodologies that will be used for different types of projects. This ensures that initiatives are managed with a consistent structure, making it easier to identify areas for improvement and implement continuous improvement processes.
- Create templates and tools: provide PMO staff with the appropriate tools to perform their work efficiently. This includes project templates, dashboards, and cloud-based tools to facilitate project planning, monitoring, and reporting.
Your PMO’s next big step starts right here
Request a demo to see how Triskell Software can help your PMO enhance efficiency, deliver projects on time, and align with business goals.
5. Implement Change Management
Implementing a PMO is not just about creating processes and forming new teams—it’s a cultural shift. To manage this change effectively, follow these guidelines:
- Communicate PMO’s objectives and scope: clearly communicate the PMO’s objectives, scope, and benefits. Address questions about how it will impact the day-to-day operations of teams.
- Overcome resistance to change: change often meets resistance, whether due to fear, mistrust, or reluctance to abandon long-standing processes. Organize informational sessions, address questions, and provide concrete examples of how the PMO will improve organizational performance.
6. Launch the PMO pilot phase
Before fully operationalizing the PMO, it is recommended to conduct a pilot phase to test and refine the established processes and methodologies.
- Select pilot projects: choose low-risk projects that represent a cross-section of the organization’s activities. These projects will serve as a controlled environment to test methodologies and workflows.
- Monitor and evaluate: closely monitor the performance of the pilot projects. Gather data and assess the effectiveness of the PMO’s management. Use KPIs to measure the PMO’s impact on project value, delivery timelines, and resource optimization.
- Gather feedback: request feedback from the teams involved in the pilot projects. What worked? What didn’t? Use this input to refine processes before expanding the PMO’s scope.
7. Scale the PMO
Finally, once the pilot phase has been successful, it is time to extend the PMO’s reach across the organization.
- Take on more projects: leverage the lessons learned from the pilot phase to expand the PMO’s coverage. This may include managing more complex projects or portfolios not included in the pilot. You may also need additional staff or tools to support this expanded scope.
- Embrace continuous improvement: Every PMO should adopt a mindset of continuous improvement. Regularly evaluate the PMO’s performance and refine its processes to adapt to organizational strategy changes or emerging trends in project management.
- Measure PMO performance: establish metrics to evaluate the PMO’s success, such as project success rates, customer satisfaction (CSAT), cycle times, estimated vs. actual costs, etc. These indicators not only drive improvement but also justify future investments and sustain senior management support.
How PMOs can leverage PPM tools to accelerate value delivery
When successfully implementing a PMO focused on delivering value, PPM tools like Triskell Software can play a key role. These solutions not only support project planning and management but also help align initiatives with strategy, improve efficiency, and provide actionable insights.
Here’s a closer look at how Triskell can enhance your PMO’s performance in key areas:
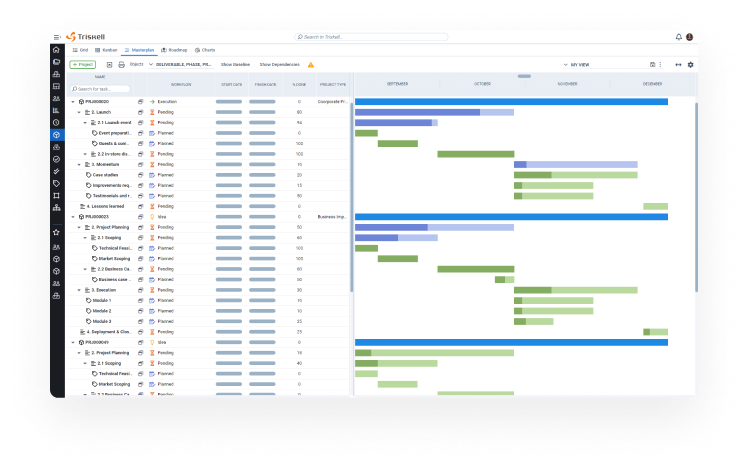
Comprehensive visibility of project portfolios
Triskell provides PMOs with a centralized PPM platform to monitor all their projects and portfolios in real-time. This level of visibility enables PMOs to:
- Ensure that each project aligns with business objectives.
- Identify initiatives that are struggling.
- Understand detailed interdependencies between projects.
- Reallocate resources as needed.
- Keep stakeholders informed about portfolio performance.
The best of Agile and Waterfall in one platform
Triskell allows you to configure and adapt the platform to your organization’s management processes and methodologies. This hybrid approach supports any framework—Agile, Waterfall, Phase Gate, or DevOps—enabling PMOs to oversee various project types from a single platform without losing visibility or control.
- Agile teams can leverage Kanban and Scrum boards to manage sprints, backlogs, and deliverables.
- Teams using traditional methodologies like Waterfall or Phase Gate can rely on a structured management approach within Triskell.
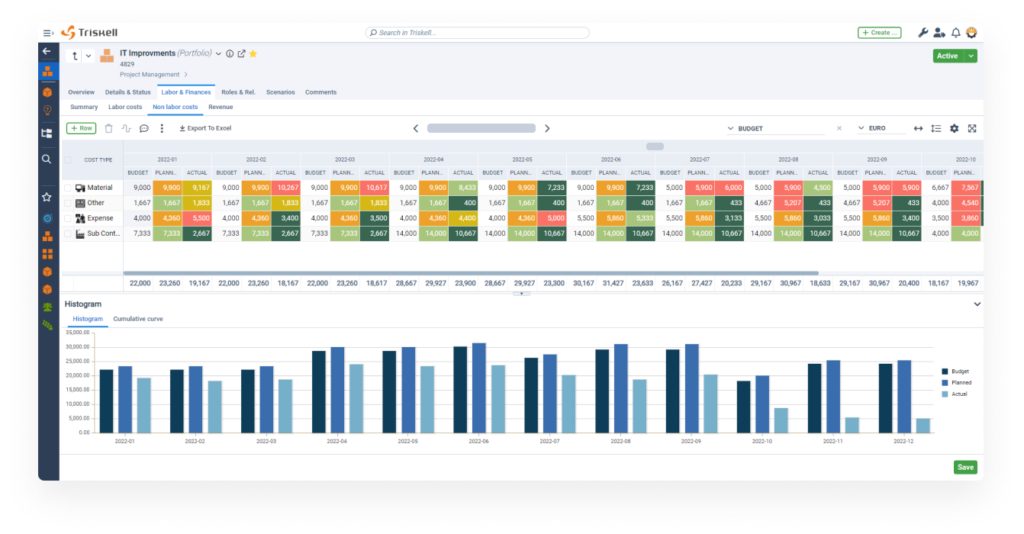
Resource and Financial Management capabilities
One of Triskell’s key strengths is its advanced integrated Resource Management and Financial Management capabilities.
- Resource Management: Track resource usage, availability, and skillsets to help your PMO reduce bottlenecks and boost team productivity.
- Financial Management: Monitor budgets in real-time, estimate costs, and compare them against actual project expenses.
Customizable reports and dashboards
Triskell lets you design reports and dashboards tailored to your needs. Whether you require high-level overviews for executives or detailed real-time metrics for specific projects, Triskell offers a wide array of dashboard options to empower your PMO.
Conclusion
PPM tools like Triskell are more than just software solutions—they are enablers of PMO success. By offering real-time visibility, supporting hybrid project methodologies, optimizing resources, and delivering customizable reporting, Triskell empowers PMOs to go beyond project management and drive strategic outcomes.
With the right tools, PMOs can deliver greater value, ensure alignment with business priorities, and become indispensable partners in the organization’s success. If your PMO aims to make a greater impact, adopting a platform like Triskell could be the first step toward achieving your goals.
Related Content

10 types of Project Management Offices (PMO): structure, purpose and how to choose the right one
Learn about different PMO types, their governance levels, and which one is the best fit for your company’s project management needs.

How to create a project budget: methods and techniques for effective project budgeting
Learn how to create a project budget with this detailed guide. Discover essential methods and techniques for effective project budgeting in PPM.

20 strategic planning models and tools for medium and large companies
Looking for the best strategic planning frameworks? This guide covers 20 proven models to enhance decision-making and business growth.
FAQ about PMO implementation
How can the success of a PMO be measured?
To measure the success of a PMO, track both qualitative and quantitative indicators. Common KPIs include project success rates, budget adherence, project completion timelines, and resource utilization rates.
You can also assess stakeholder satisfaction through surveys and monitor improvements in project delivery consistency and alignment with strategic objectives.
What are the costs associated with the implementation of a PMO?
The cost of establishing a PMO depends on the scope and size of the organization. Initial expenses may include PMO staff salaries, training costs, software platforms, and technology infrastructure. Recurring costs typically include:
- Staff training.
- Acquisition of additional resources.
- Software licenses.
However, the ROI for a PMO often offsets these costs by improving project success rates and operational efficiency.
What tools or software can enhance PMO efficiency?
PPM (Project Portfolio Management) tools like Triskell can significantly enhance PMO efficiency by providing centralized access to project data, performance analytics, resource allocation, and reporting functions.
Other tools, such as communication platforms and task management software, further streamline project workflows and facilitate collaboration.

